In this section, some of the traditional beliefs and natural remedies practiced by traditional Chinese, Indian, and Korean families in New Zealand are discussed.
The belief in body balance is similar to homeostasis in that there are external influences, which can affect your health. The four main elements are wind, heat, dampness and toxins, which can exist in every type of activity, environment or food. If the body has an excess of any one of these elements, or a disruption of internal harmonies, it can lead to ill health. For example, western medicines are believed to have a heat nature to them. To counter this, patients may take herbal teas or medicines to reduce the effect of heat in their bodies.
Usually alternative medicines or treatments are used to target the root cause of a disease or to re-establish body balance. The types of alternative treatments used are:
- Daily diet, herbal teas, herbal tonics/medicines, supplements.
- Homeopathy, relaxation.
- Qi Qong, Tai Chi.
- Acupuncture, acupressure.
- Traditional Chinese Medicine or Ayurvedic Medicine.
Yin-Yang

Yin-Yang is about believing in two opposing forces consisting of five material agents. These opposite forces either produce one another or overcome one another cyclically and constantly. Therefore all opposites of experience, such as health and sickness, wealth and poverty, can be explained in reference to the temporary dominance or one principle over the other. Since no one principle dominates eternally, that means that all conditions are subject to change into their opposites.
Qi Qong

(Chi Kung) The name means to cultivate energy or to do energy work. It is an integration of physical postures, breathing techniques and mental focus all of which are aimed at easing or increasing the flow of chi, or directing chi to specific systems or organs within the body. It is sometimes classified as a marital art, and can have medical and spiritual effects.
Acupressure

It is a form of touch therapy that utilises the principles of acupuncture and Chinese medicine. In acupressure, the same points on the body are used as in acupuncture, but are stimulated with finger pressure (or a blunt tool) instead of with the insertion of needles. It is used to relieve a variety of symptoms and pain.
Scraping

(Scraping Sand) Scraping was a popular treatment around 3,000 years again in rural areas of China. The technique was slowly forgotten with the advance of modern medicine, but is still sometimes practiced by housewives.
The theory behind this treatment is that scraping will re-activate the body’s healing mechanism in order to help clear any blockages due to dead blood cells and debris from accident areas and to allow proper circulation. Scraped areas are chosen according to acupuncture points and affected sites.
This treatment is used for physical discomforts such as headaches, joint pain, muscle aches and even bloating. (It may leave marks on the body, not to be assumed a result of physical abuse).
Coining
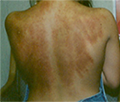
Coining (gua sha), is a traditional Chinese medical treatment in which the skin is scraped to produce light bruising. Practitioners believe gua sha releases unhealthy elements from injured areas and stimulates blood flow and healing (Wikipedia, 2016).
Gua sha was transferred and translated into Vietnamese from China as cạo gió. This term translates roughly "to scrape wind", as in Vietnamese culture "catching a cold" or fever is often referred to as trúng gió, "to catch wind". Cạo gió is an extremely common remedy in Vietnam and for expatriate Vietnamese. There are many variants of cạo gió. Some methods use oil balm and a coin to apply pressure to the skin. Others use a boiled egg with a coin inserted in the middle of the yolk. The egg is wrapped in a piece of cloth and rubbed over the forehead (in the case of a fever) and other areas of skin. After the rubbing, the coin is removed from the egg and will appear blackened (Wikipedia, 2016).
Ayurvedic
Restores and maintains the balance of the 3 elements in the body (aspects of the Life Force) referred to as doshas: pitta, vatta, and kapha. The rhythms of the pulse as well as clinical history and observation are used in diagnosis. Herbs, oils, dietary management, detoxification, and some massage regimes are included in treatment.
This medicine system is traditional in India and there are a number of practitioners in New Zealand (including Westerners who are being locally trained).